ICC CAS has made significant progress in the research of CO₂ low-temperature methanation catalysts
Recently, team led by Prof. Fukui Xiao and Ning Zhao from Institute of Coal Chemistry Chinese Academy of Sciences (ICCCAS) conduct the research on the inverse ZrO2/Ni catalysts for CO2 methanation and the related reaction mechanism. The results were published in Advanced Functional Materials with the title of "The Inverse Configuration Confers High Activity and Stability to ZrO2/Ni Catalysts for CO2 Methanation".
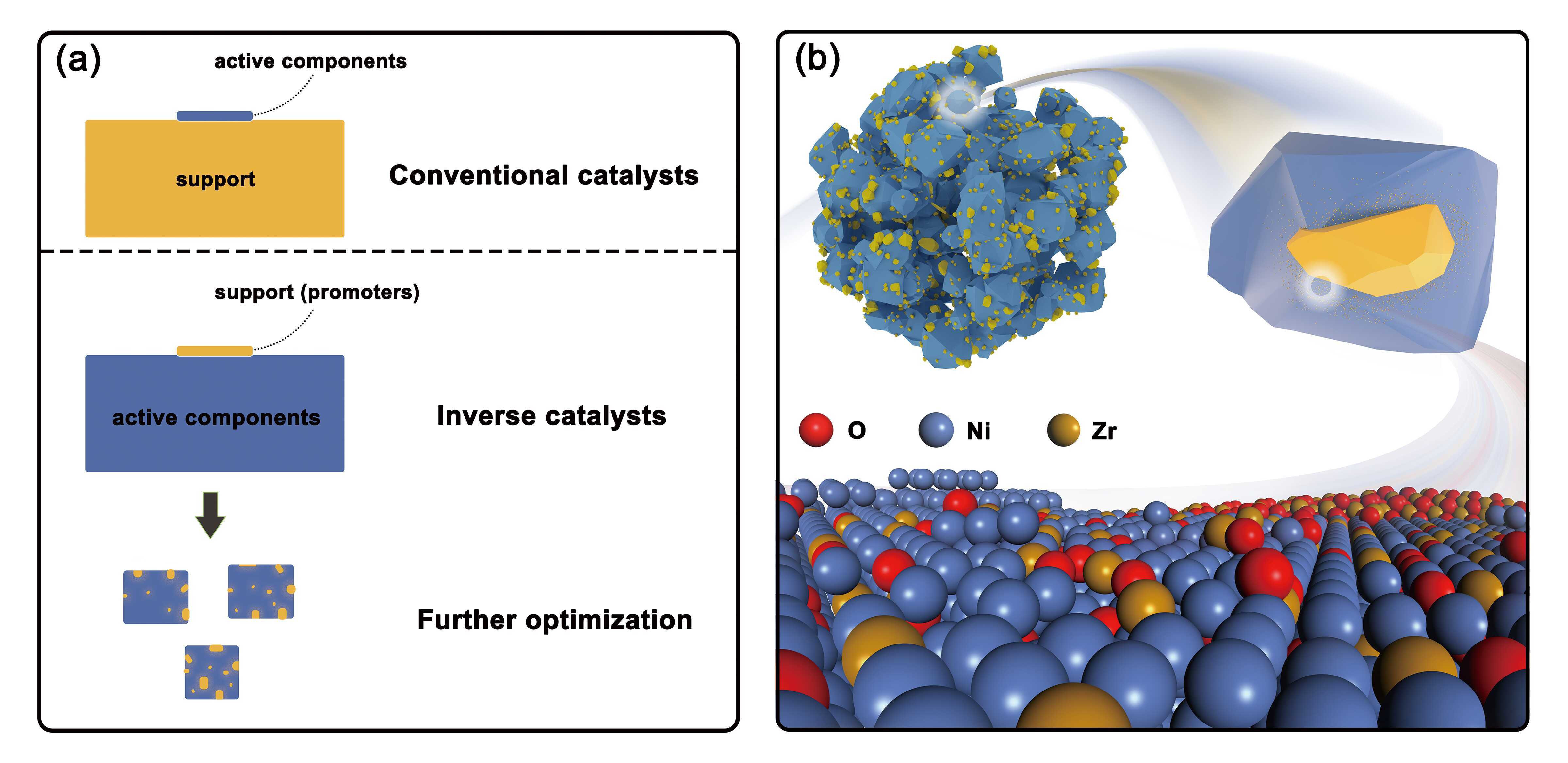
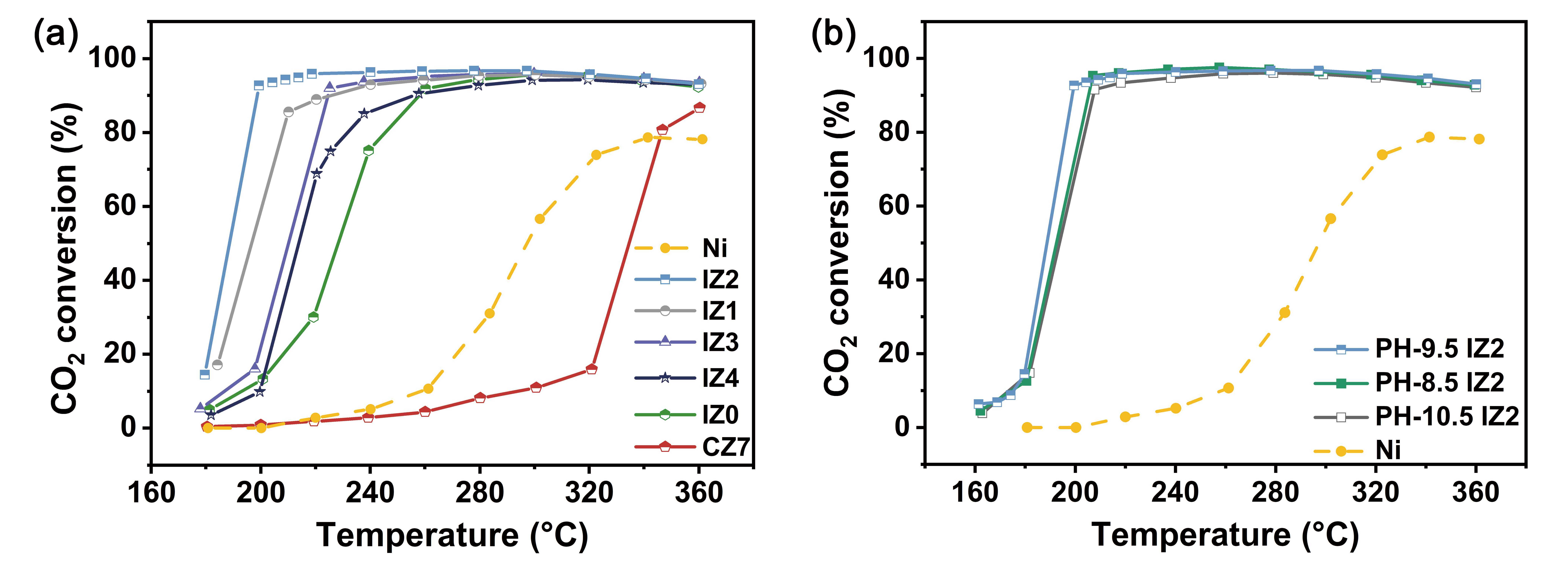
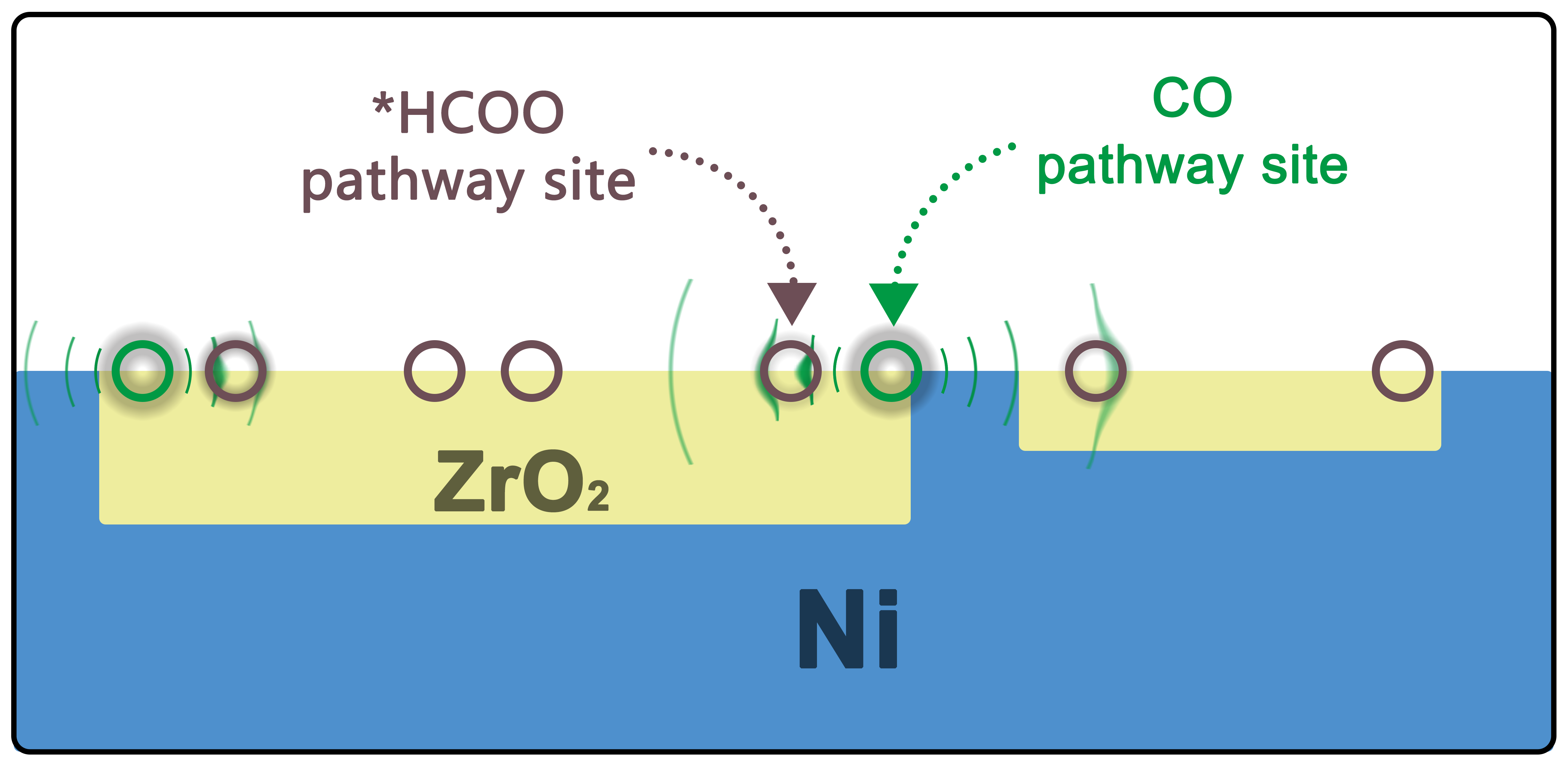
ABSTRACT: The low-temperature activity and stability of the catalyst are crucial for the CO2 methanation process. In this study, an inverse ZrO2/Ni catalyst is synthesized to regulate the metal-oxide interaction by tuning the Ni/Zr ratio. The optimized catalyst exhibited exceptional performance, achieving a CO2 conversion rate of 92% and a methane selectivity of ≈100% at 200 °C. Furthermore, the catalyst demonstrated remarkable stability. Comparative analysis with pure nickel and conventional catalysts revealed that the better low-temperature activity of the inverse catalyst is due to the substantial amount of nickel providing strong H2 dissociation capability as well as additional hydrogen spillover effect, which reduced part of the ZrO2, thereby creating more oxygen vacancies as adsorption and reaction sites for CO2. Both the CO and *HCOO pathways are present and synergistically interact. The high stability is attributed to the straightforward and homogeneous structure. The effect of coke deposition on the different reaction pathways is also discussed. The relatively simple synthesis method in this study may result in lower cost and enhanced safety, which are crucial for industrial applications.
https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202425888
© Institute of Coal Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, All Rights Reserved
Address: 27 South Taoyuan Road, Taiyuan, Shanxi, P.R.China
Tel: (86)351-4041627 Email: sxicc_en@sxicc.ac.cn